

Views: 2 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-11 Origin: Site











Win customer trust with efficiency and professionalism. In early October 2025, we successfully signed a procurement contract for UNS S31254 stub end with a foreign client. The successful signing of the order is attributed to professional and efficient communication.
The customer requested our assistance in clarifying the terminal procurement needs, and we quickly provided the customer with accurate answers because we have a lot of experience. 6MO, A182 F44, A403 WPS UNS 31254 all refer to the same material: UNS S31254; At the same time, the customer introduced the connection function between the stub end and the lap joint flange, and provided a quotation.
The customer recognized our professional answers and quotations, eliminated concerns, and both parties successfully signed the contract. This cooperation has verified the importance of professional interpretation, patient communication, and reasonable pricing in winning customer trust.
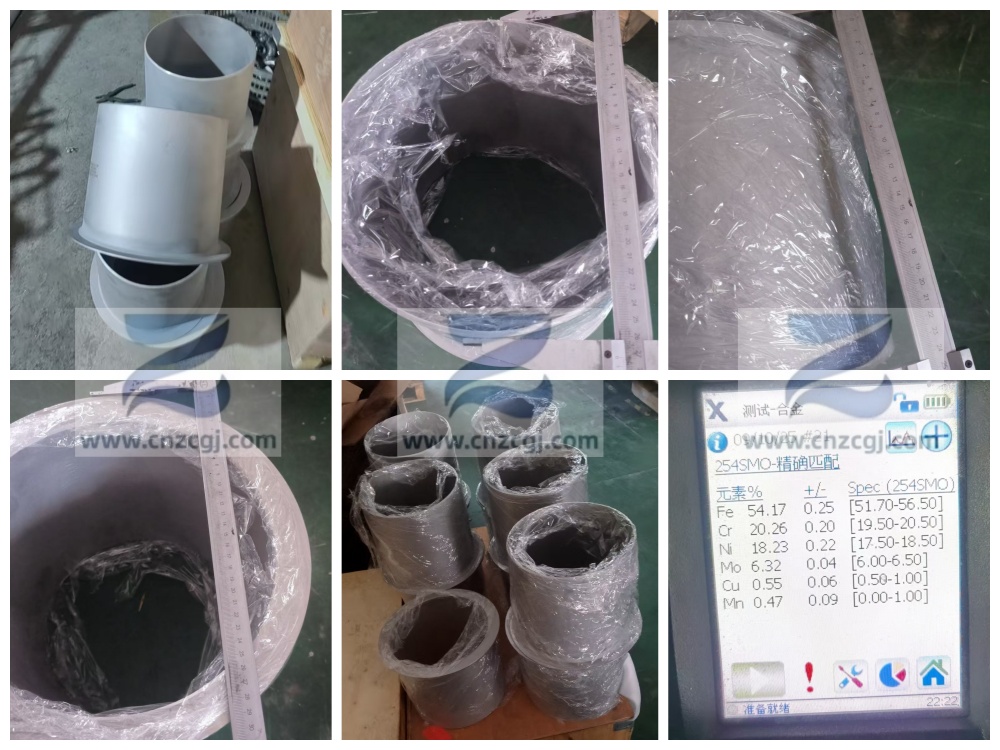

UNS S31254 is a designation for a high alloy austenitic stainless steel in the United States Unified Numbering System (UNS), corresponding to the international standard EN 1.4547 stainless steel, commonly referred to as "254SMO" in China. This material belongs to the category of super austenitic stainless steel and has excellent corrosion resistance.
CHEMICAL | LIMITS | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Ni | Cr | Mo | N | Cu |
ASTM A403 WP31254 | MIN | 17.50 | 19.50 | 6.00 | 0.18 | 0.50 | |||||
MAX | 0.02 | 1.00 | 0.030 | 0.010 | 0.80 | 18.50 | 20.50 | 6.50 | 0.25 | 1.00 |
Chromium content enhances corrosion resistance, while molybdenum and nitrogen elements increase resistance to strong corrosive substances.
UNS S31254, with its unique chemical element composition ratio, distinguishes its performance from ordinary austenitic stainless steels such as SS304 and SS316
As one of the representatives of super austenitic stainless steel, UNS S31254 has a variety of materials with similar compositions and properties in the market, mainly divided into two categories: "international standard corresponding materials" and "same type super austenitic stainless steel", which can be selected according to specific working conditions, procurement convenience, and cost requirements:
China | Japan | American | International | Europan | Sweden | |||
GB | ISC | JIS | ASTM | UNS | ISO | EN | 数字牌号 | SS |
015Cr20Ni18Mo6CuN | S31252 | SUS 312L | S31254 | S31254 | X1CrNiMoN 20-18-7 | X1CrNiMoCuN 20-18-7 | 1.4547 | 254SMO |
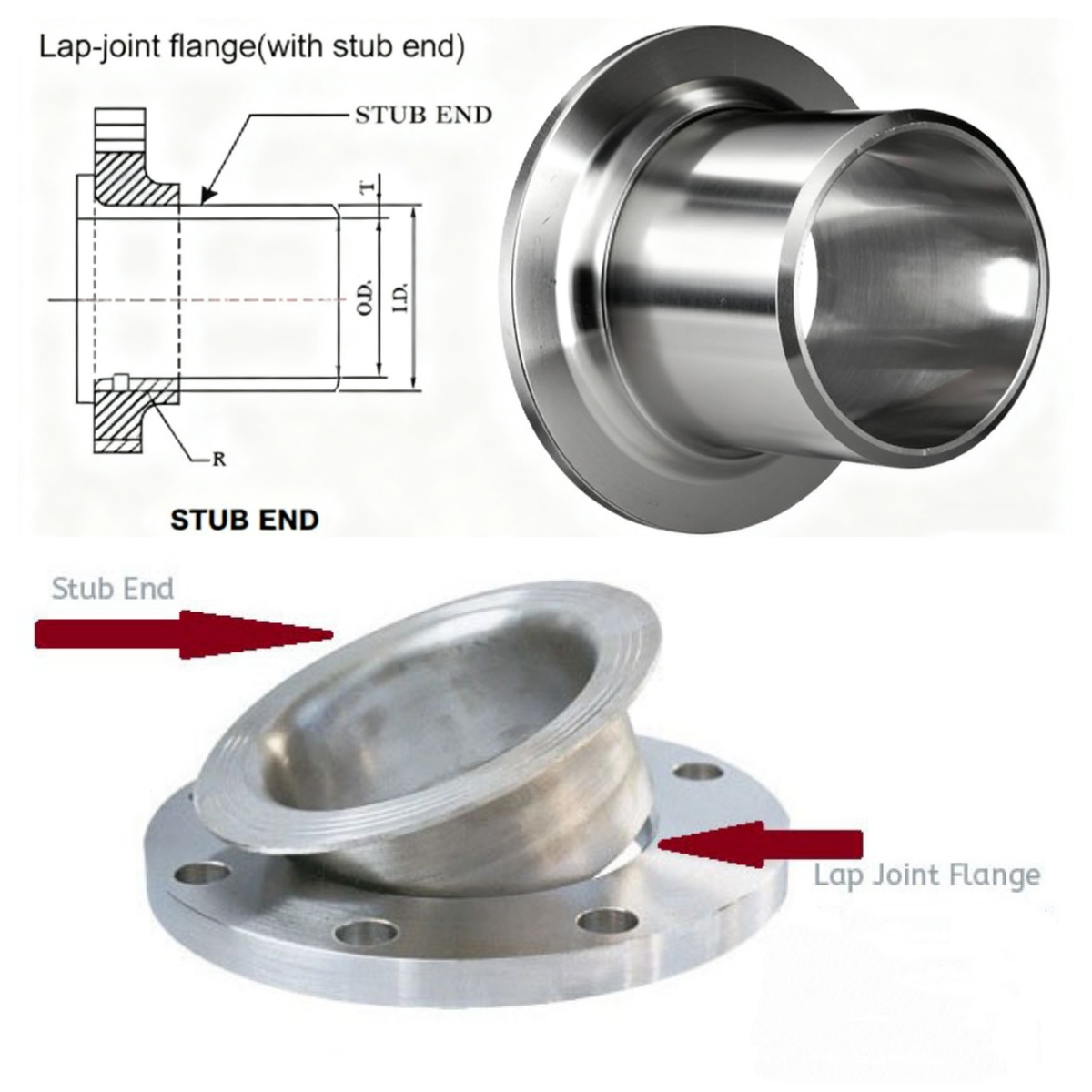

ASME B16.9 stub end is a type of butt welded pipe fittings that is generally used in conjunction with loose flanges to achieve flange connections in pipeline systems. The flange short section is generally formed by stamping process, and is divided into long flange and short flange according to the length of the straight pipe end. The production standards for flange short sections mainly comply with the American production standards ANSI/ASME B16.9 and MSS SP-43.
The stainless steel flange short sections in ASME B16.9 standard can be divided into long stub ends and short stub ends based on their length and shape.
Compact structure: Compared to integral flanges, there is no need for independent flanges, reducing the space occupied by pipe fittings and adapting to narrow installation environments;
Uniform force distribution: The flange and short tube are integrated into a single piece, resulting in high overall strength after welding, which can disperse the pressure and vibration loads of the pipeline system;
Reliable sealing: The flange surface of the flange is tightly fitted with the loose flange, and the sealing gasket can effectively prevent medium leakage, especially suitable for medium and low pressure working conditions;
Cost controllable: No need to use full-size flanges, reducing the consumption of valuable materials (such as stainless steel) and lowering procurement costs.
The core manufacturing standard for flange short sections is ASME B16.9 (American Society of Mechanical Engineers standard), which strictly specifies the material, dimensional tolerances, processing technology, inspection requirements, etc. of flange short sections:
Material requirements: including carbon steel (such as A234 WPB), stainless steel (such as A403 WP304/316), alloy steel, and other materials;
Processing specifications: It is stipulated that cold stamping or hot forging processes must be used for flanging forming;
Inspection requirements: Before leaving the factory, visual inspection, dimensional testing, hydrostatic testing, etc. must be carried out.
The stub end needs to be combined with a lap joint flange to form a detachable connection structure: first, the straight end of the flange short section is welded and fixed to the pipeline, and then the loose flange is placed on the outside of the flange end of the flange short section. The loose flange is pressed against the docking flange with bolts, and the sealing is achieved by the compression of the flange surface and gasket.
This combination method does not require the flange to be directly welded to the pipeline, avoiding damage to the pipeline material caused by high welding temperatures. The loose flange can be flexibly adjusted in position, simplifying the installation and maintenance process, especially suitable for pipeline systems such as stainless steel and non-ferrous metals that are prone to deformation after welding.
The size of the UNS S31254 stub end should match the nominal size (NPS) of the pipeline and comply with the requirements of ASME B16.9 standard.
ASME B16.9 stub end sizes: 1/2 "to 24",
Thickness :SCH10,SCH20,STD,SCH40,SCH60,SCH80,SCHXS,SCH100,SCH120,SCH140,SCH160,SCHXXS.
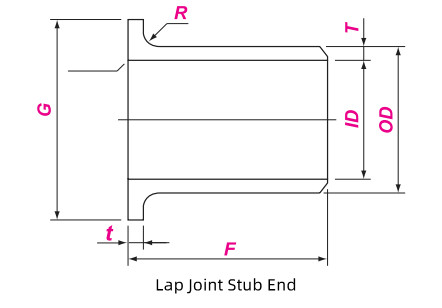
DN | NPS | OD | F | R | G | SCH40 WEIGHT | ||||
Max. | Min. | Long Type | Short Type | A | Bmax | LP (kg) | SP (kg) | |||
15 | 1/2 | 22.8 | 20.5 | 76 | 51 | 3 | 0.8 | 35 | 0.12 | 0.09 |
20 | 3/4 | 28.1 | 25.9 | 76 | 51 | 3 | 0.8 | 43 | 0.16 | 0.12 |
25 | 1 | 35.0 | 32.6 | 102 | 51 | 3 | 0.8 | 51 | 0.32 | 0.18 |
32 | 11/4 | 43.6 | 41.4 | 102 | 51 | 5 | 0.8 | 64 | 0.43 | 0.25 |
40 | 11/2 | 49.9 | 47.5 | 102 | 51 | 6 | 0.8 | 73 | 0.52 | 0.31 |
50 | 2 | 62.4 | 59.5 | 152 | 64 | 8 | 0.8 | 92 | 1.02 | 0.52 |
65 | 21/2 | 75.3 | 72.2 | 152 | 64 | 8 | 0.8 | 105 | 1.60 | 0.81 |
80 | 3 | 91.3 | 88.1 | 152 | 64 | 10 | 0.8 | 127 | 2.11 | 1.10 |
90 | 31/2 | 104.0 | 100.8 | 152 | 76 | 10 | 0.8 | 140 | 2.55 | 1.52 |
100 | 4 | 116.7 | 113.5 | 152 | 76 | 11 | 0.8 | 157 | 3.05 | 1.80 |
125 | 5 | 144.3 | 140.5 | 203 | 76 | 11 | 1.6 | 186 | 5.42 | 2.25 |
150 | 6 | 171.3 | 167.5 | 203 | 89 | 13 | 1.6 | 216 | 7.02 | 3.59 |
200 | 8 | 222.1 | 218.3 | 203 | 102 | 13 | 1.6 | 270 | 10.6 | 5.98 |
250 | 10 | 277.2 | 272.3 | 254 | 127 | 13 | 1.6 | 324 | 18.4 | 10.2 |
300 | 12 | 328.0 | 323.1 | 254 | 152 | 13 | 1.6 | 381 | 22.8 | 14.9 |
350 | 14 | 359.9 | 354.8 | 305 | 152 | 13 | 1.6 | 413 | 28.7 | 15.8 |
400 | 16 | 411.0 | 405.6 | 305 | 152 | 13 | 1.6 | 470 | 33.1 | 18.9 |
450 | 18 | 462.0 | 456.0 | 305 | 152 | 13 | 1.6 | 533 | 38.0 | 22.0 |
500 | 20 | 514.0 | 507.0 | 305 | 152 | 13 | 1.6 | 584 | 42.3 | 24.3 |
550 | 22 | 565.0 | 558.0 | 305 | 152 | 13 | 1.6 | 641 | - | - |
600 | 24 | 616.0 | 609.0 | 305 | 152 | 13 | 1.6 | 692 | 51.2 | 29.6 |
Petrochemical Industry
Municipal Engineering
Energy Sector
Food and Pharmaceutical Industry
Ship and Ocean Engineering