

Views: 7 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-10 Origin: Site











In the design and construction of industrial pipeline systems, welded pipe fittings play a crucial role. Whether their quality and performance meet the operational requirements of the pipeline system directly determines the safety, stability, and service life of the entire system.
ASME B16.9 SS316 butt weld elbow, as one of the most widely used pipeline fittings, is made of high-quality stainless steel material and strictly manufactured in accordance with international standards. With its excellent performance, size, and wide applicability, it has become an important accessory in the industrial pipeline field.
The ASME B16.9 standard is a standard specification developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) for forged steel butt welded pipe fittings manufactured in factories. It has high authority and recognition worldwide.
This standard strictly regulates the materials, dimensions, tolerances, wall thickness, ports, pressure and temperature ratings, inspection and testing methods, and other aspects of welded pipe fittings. From the chemical composition and mechanical performance requirements of materials, to the dimensional details such as outer diameter, wall thickness deviation, and angle tolerance of pipe fittings, to non-destructive testing, hydrostatic testing, and other inspection processes, each requirement has been scientifically demonstrated and practically tested to ensure that pipe fittings can operate safely and reliably under various complex working conditions.
SS316 butt weld elbow produced in accordance with ASME B16.9 standards can not only meet the industrial needs of different countries and regions, achieve standardized interchangeability of pipe fittings, but also provide great convenience for the design, installation, and maintenance of pipeline systems, effectively reducing safety risks and cost investment in industrial production.
ASME B16.9 SS316 butt weld elbow is made of high-quality SS316 stainless steel pipes as raw materials and manufactured through advanced production processes. Its surface is smooth and flat, with high precision in welding port processing. The groove angle and blunt edge size meet the requirements of ASME B16.9 standard; The curved part has a smooth transition, no wrinkles or deformations, a compact overall structure, and a beautiful appearance.
This type of elbow is mainly used in industrial pipeline systems such as petroleum, chemical, and power industries. With accurate welding port design, it is easy to firmly weld with pipelines, ensuring joint strength and sealing; The smooth curved shape effectively reduces fluid resistance, improves transportation efficiency, not only has good practicality, but also enhances the overall aesthetics of the pipeline system.
Stainless steel butt weld elbow can be classified into various types according to different classification methods, and the common ones mainly include the following:
Classified by Bending Angle

90 deg BW elbow: The most widely used in industrial pipeline systems, with a bending angle of 90 deg. The characteristic is that it can achieve vertical turning of the pipeline, change the direction of pipeline transportation, and during the turning process, the fluid resistance is relatively small, and the flow field is stable.

45 deg butt weld elbow: With a bending angle of 45 deg, compared to a 90 deg elbow, it has less fluid resistance and lower pressure loss when passing through. The characteristic is that it is suitable for situations where pipelines require small angle turning, which can make the flow of fluid in the pipeline smoother and reduce the erosion of the inner wall of the pipeline.

180 deg elbow: also known as a U-shaped elbow, with a bending angle of 180 deg, can achieve reverse transportation of the pipeline, allowing fluid to form back flow in the pipeline. The characteristics are symmetrical structure, regular flow trajectory of fluid in curved parts, uniform distribution of resistance, and good fatigue resistance and impact resistance.
Classified by Radius

Long radius : Its bending radius R is equal to 1.5 times the outer diameter of the pipeline (R=1.5D, D is the outer diameter of the pipeline). The characteristic is that the flow resistance of the fluid passing through the elbow is small, the flow field distribution is uniform, which can effectively reduce the flushing and wear of the fluid on the inner wall of the elbow, and extend the service life of the elbow. At the same time, the long radius design provides better stress conditions for the elbow, and has stronger compressive strength when subjected to higher pressures.
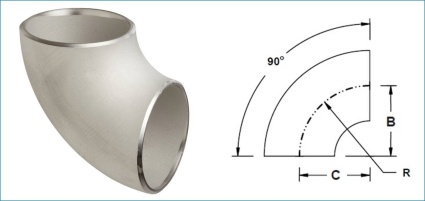
Short radius : The curvature radius R is equal to the outer diameter of the pipeline (R=1D). The characteristics are compact structure, small space occupation, and flexible use in situations where pipeline installation space is limited. However, due to its small curvature radius, the resistance of the fluid passing through is relatively high, and the pressure loss is also high, resulting in severe erosion of the inner wall of the pipeline.
SS316 stainless steel is a common austenitic stainless steel material, which has many significant advantages in performance compared to SS304 stainless steel, laying a solid foundation for the high-quality performance of ASME B16.9 SS316 butt weld elbow.
Excellent corrosion resistance: Molybdenum is added to SS316 stainless steel, which can significantly improve its corrosion resistance in harsh corrosive environments, especially in environments containing chloride ions such as seawater, saltwater, chloride solutions, etc. It can effectively resist point corrosion, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking caused by chloride ions. This makes SS316 butt welded elbows irreplaceable in the treatment of chlorine containing media in marine engineering, seawater desalination, chemical industries, and other scenarios. They can maintain good performance for a long time and are not easily corroded or damaged.
Good high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance: SS316 stainless steel can maintain high strength and hardness in high-temperature environments, and its high-temperature creep strength and endurance strength are superior to SS304 stainless steel. At the same time, SS316 stainless steel has excellent oxidation resistance at high temperatures, forming a dense oxide film that prevents further reaction between oxygen and the interior of the metal, effectively resisting high-temperature oxidation corrosion. Therefore, ASME B16.9 SS316 butt weld elbow can operate stably under high temperature conditions (such as petroleum refining, chemical reaction equipment, power boilers, and other high-temperature pipeline systems) without performance degradation or damage caused by high temperature.
Chemical Composition
| CHEMICAL | LIMITS | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Ni | Cr | Mo |
| SS316L | MIN | 10.00 | 16.00 | 2.00 | |||||
| MAX | 0.03 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 14.00 | 18.00 | 3.00 |
Excellent mechanical performance: SS316 stainless steel has high tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation, and can withstand large external forces and pressure fluctuations in pipeline systems. It has good impact resistance and fatigue resistance. During the operation of the pipeline system, even under external forces such as vibration and impact, SS316 butt welded elbows are not prone to deformation, rupture, and other faults, ensuring the stability and safety of the pipeline system.
Good processing performance: SS316 stainless steel has excellent forging, welding, cutting and other properties, making it easy to manufacture various shapes and sizes of butt welded elbows. During the welding process, the welded joints of SS316 stainless steel have good strength and sealing, which can meet the requirements of ASME B16.9 standard for welding quality, ensuring a firm and reliable connection between the welded elbow and the pipeline.
Mechanical Properties
| MATERIAL | SS316L |
| T.S (MPA) | 485 min |
| Y.S (MPA) | 170 min |
| EL % | 28 min |
ASME B16.9 SS316 butt weld elbow strictly follow standard requirements in terms of size, with extremely high precision and consistency, providing strong support for the installation and operation of pipeline systems.
Outer diameter and wall thickness dimensions: The deviation of the outer diameter and wall thickness dimensions of the butt welded elbow is strictly controlled within the range specified in ASME B16.9 standard, ensuring that it matches the outer diameter and wall thickness of the supporting pipeline and can achieve seamless docking. The outer diameter and wall thickness dimensions not only facilitate positioning and welding operations during installation, but also ensure the overall strength and sealing of the pipeline system, avoiding problems such as leakage and pressure loss caused by size mismatch.
Angle tolerance: Whether it is a 90 deg, 45 deg, or 180 deg butt weld elbow, its angle tolerance is very small, usually controlled within ± 0.5 (depending on the standard grade requirements). Accurate angles can ensure the accuracy of pipeline turning, allowing fluid to flow smoothly in the designed direction, reducing additional resistance and flow field turbulence caused by angle deviation, and improving the transportation efficiency of pipeline systems.
Bending radius : The curvature radius of long radius and short radius butt weld elbow is strictly manufactured according to the dimensions specified in ASME B16.9 standard. The deviation of curvature radius is small, which can ensure that the flow trajectory of fluid passing through the elbow meets the design requirements, reduce the flushing and wear of fluid on the inner wall of the elbow, and also facilitate stress calculation and design of the pipeline system, ensuring the stress balance of the pipeline system during operation.
Welding end size specification: The welding end (groove) size of the butt welded elbow (such as groove angle, blunt edge thickness, root gap, etc.) strictly follows the requirements of ASME B16.9 standard and relevant welding specifications to ensure a good welding joint can be formed when welding with the pipeline. Standardized welding end dimensions can improve welding quality, enhance the strength and sealing of welded joints, and effectively prevent the occurrence of welding defects such as incomplete penetration, incomplete fusion, porosity, cracks, etc.
ASEM B16.9 strictly specifies the size parameters of butt welded elbows, including:
Nominal Size (DN): ranging from DN15 (1/2 inch) to DN2000 (80 inches), covering most industrial pipeline requirements.
Wall thickness grade: Following the SCH standard, common grades include SCH10, SCH20, SCH40, SCH80, etc. The wall thickness increases with the grade, and the corresponding grade can be selected according to the pipeline pressure.

Nominal Size | Outside Diameter at Bevel | Center to End | Center to Center | Back to Face | |||||
90° Elbows | 45° Elbows |
| |||||||
DN | NPS | OD | A | B | O | K | |||
LR | SR | LR | LR | SR | LR | SR | |||
15 | 1/2 | 21.3 | 38 | 16 | 76 | 48 | |||
20 | 3/4 | 26.7 | 38 | 19 | 76 | 51 | |||
25 | 1 | 33.4 | 38 | 25 | 22 | 76 | 51 | 56 | 41 |
32 | 1 1/4 | 42.2 | 48 | 32 | 25 | 95 | 64 | 70 | 52 |
40 | 1 1/2 | 48.3 | 57 | 38 | 29 | 114 | 76 | 83 | 62 |
50 | 2 | 60.3 | 76 | 51 | 35 | 152 | 102 | 106 | 81 |
65 | 2 1/2 | 73.0 | 95 | 64 | 44 | 190 | 127 | 132 | 100 |
80 | 3 | 88.9 | 114 | 76 | 51 | 229 | 152 | 159 | 121 |
90 | 3 1/2 | 101.6 | 133 | 4、89 | 57 | 267 | 178 | 184 | 140 |
100 | 4 | 114.3 | 152 | 102 | 64 | 305 | 203 | 210 | 159 |
125 | 5 | 141.3 | 190 | 127 | 79 | 381 | 254 | 262 | 197 |
150 | 6 | 168.3 | 229 | 152 | 95 | 457 | 305 | 313 | 237 |
200 | 8 | 219.1 | 305 | 203 | 127 | 610 | 406 | 414 | 313 |
250 | 10 | 273.0 | 381 | 254 | 159 |
| 508 | 518 | 391 |
300 | 12 | 323.8 | 457 | 305 | 190 | 914 | 609 | 619 | 467 |
350 | 14 | 355.6 | 533 | 356 | 222 | 1067 | 711 | 711 | 533 |
400 | 16 | 406.4 | 610 | 406 | 254 | 1219 | 813 | 813 | 610 |
450 | 18 | 457.0 | 686 | 457 | 286 | 1372 | 914 | 914 | 686 |
500 | 20 | 508.0 | 762 | 508 | 318 | 1524 | 1016 | 1016 | 762 |
550 | 22 | 559.0 | 838 | 559 | 343 | 1676 | 1118 | 1118 | 838 |
600 | 24 | 610.0 | 914 | 610 | 381 | 1829 | 1219 | 1219 | 914 |
650 | 26 | 660.0 | 991 | 660 | 406 | ||||
700 | 28 | 711.0 | 1067 | 711 | 438 | ||||
750 | 30 | 762.0 | 1143 | 762 | 470 | ||||
800 | 32 | 813.0 | 1219 | 813 | 502 | ||||
850 | 34 | 864.0 | 1295 | 864 | 533 | ||||
900 | 36 | 914.0 | 1372 | 914 | 565 | ||||
950 | 38 | 965.0 | 1448 | 965 | 600 | ||||
1000 | 40 | 1016.0 | 1524 | 1016 | 632 | ||||
1050 | 42 | 1067.0 | 1600 | 1067 | 660 | ||||
1100 | 44 | 1118.0 | 1676 | 1118 | 695 | ||||
1150 | 46 | 1168.0 | 1753 | 1168 | 727 | ||||
1200 | 48 | 1219.0 | 1829 | 1219 | 759 | ||||
Tolerance range: The outer diameter and wall thickness of the welding end must meet the standards to ensure the fit with the pipeline during welding and reduce welding defects. The ASME B16.9 butt weld elbow standard also specifies tolerances for the center distance and end face perpendicularity of the elbow to ensure installation accuracy.
Nominal Size | All Fittings | 45°&90° Elbows |
| ||||
DN | NPS | OD 3) 4) | ID 3) | A B C M |
| K | U |
15-65 | 1/2 -21/2 | +1.6 | ± 0.8 | ± 2 | ± 6 | ± 6 | ± 1 |
80-90 | 3-31/2 | ± 1.6 | ± 1.6 | ± 2 | ± 6 | ± 6 | ± 1 |
100 | 4 | ± 1.6 | ± 1.6 | ± 2 | ± 6 | ± 6 | ± 1 |
125-200 | 5-8 | +2.4 | ± 1.6 | ± 2 | ± 6 | ± 6 | ± 1 |
250-450 | 10-18 | +4.0 | ± 3.2 | ± 2 | ± 10 | ± 6 | ± 2 |
500-600 | 20-24 | +6.4 | ± 4.8 | ± 2 | ± 10 | ± 6 | ± 2 |
650-750 | 26-30 | +6.4 | ± 4.8 | ± 3 | --- | --- | --- |
800-1200 | 32-48 | +6.4 | ± 4.8 | ± 5 | --- | --- | --- |
1300-1500 | 52-60 | +6.4 | ± 4.8 | ± 5 | --- | --- | --- |
1600-1700 | 64-68 | +6.4 | ± 4.8 | ± 5 | --- | --- | --- |
1800-2000 | 72-80 | +6.4 | ± 4.8 | ± 5 | --- | --- | --- |

In industrial pipeline systems, butt welded elbows and socket elbows are two common types of elbow fittings, which have significant differences in connection methods, structural characteristics, and applicable scenarios. Understanding these differences can help to make reasonable choices based on actual needs.
Different connection methods: This is the core difference between the two. The butt welded elbow adopts a welding connection method, that is, the two ends of the elbow are connected to the end of the pipeline through welding technology. The welding joint can withstand high pressure and tension, and the connection is firm and reliable. The socket elbow adopts the socket connection method, that is, one end of the pipeline is inserted into the socket of the elbow, and then fixed by threads, flanges or welding (socket welding), etc. The connection process is relatively simple and fast.
The structural characteristics are different: the two ends of the butt welded elbow are welding ports, and the ports are processed with grooves for easy welding operations. The overall structure is relatively simple and compact, without obvious socket structures. The socket elbow has a clear socket structure, and there is usually a sealing groove inside the socket to place a sealing ring to improve the sealing of the connection. Its structure is relatively complex, and its volume and weight are usually slightly larger than those of butt welded elbows.
Applicable pipeline sizes vary: Welding elbows are suitable for various sizes of pipelines, whether it is small-diameter pipelines (such as DN15) or large-diameter pipelines (such as DN2000 and above), corresponding welding elbow products can be found, and they are more widely used in large-diameter pipeline systems. Socket elbows are mainly suitable for small-diameter pipeline systems, generally applicable to pipelines of DN50 and below. For large-diameter pipelines, due to the difficulty of socket connections and the difficulty in ensuring connection strength, socket elbows are usually not used.
The difficulty of installation and maintenance is different: the installation of butt welded elbows requires professional welding personnel and equipment, the welding process is relatively complex, the installation cycle is long, and it is difficult to disassemble after welding, making maintenance and replacement difficult. The installation of socket elbows is relatively simple, especially those with threaded connections, which do not require professional welding skills, have fast installation speed, and are relatively easy to disassemble when maintenance or replacement is needed (threaded connections). However, the disassembly of socket elbows with socket welding connections is also relatively difficult.
The sealing requirements are different: the sealing of butt welded elbows mainly depends on the quality of the welded joints. As long as the welding quality is qualified, the sealing can be effectively guaranteed, which is suitable for pipeline systems with high sealing requirements, such as pipelines transporting toxic, harmful, flammable and explosive media. The sealing performance of socket elbows mainly depends on the sealing ring (threaded connection) or welding quality (socket welding connection). For socket elbows with threaded connections, the sealing ring is prone to aging and wear, resulting in relatively poor sealing performance. It is suitable for low-pressure pipeline systems with low sealing requirements; Although the sealing performance of socket elbows connected by socket welding has been improved, they are still not as reliable as butt welded elbows.
ASME B16.9 SS316 butt weld elbow have been widely used in various industrial fields due to their excellent performance, size, and reliable quality, mainly including the following aspects:
Petrochemical industry: suitable for transporting highly corrosive, high-temperature and high-pressure media such as crude oil and chemical raw materials, widely used in process and reaction equipment pipelines.
Natural gas industry: resistant to pressure and hydrogen sulfide corrosion, used in long-distance pipelines, urban gas and other systems.
Power industry: capable of withstanding high temperature and high pressure steam, ensuring the safe operation of power boilers and turbine pipelines.
Water treatment industry: With excellent resistance to chloride ion corrosion, it is used for seawater desalination and sewage treatment pipelines.
The pharmaceutical and food industry: meets hygiene standards, has easy to clean surfaces, and ensures production hygiene and safety.
Marine engineering for ships: resistant to seawater corrosion, with excellent mechanical properties, applied to ship power and offshore platform transportation pipelines.
ASME B16.9 SS316 butt weld elbow has become an indispensable high-quality pipe fitting product in industrial pipeline systems due to its quality that meets international high standards, excellent material performance, wide size range, rich variety, and wide application range. Whether you are in traditional industries such as petrochemicals, natural gas, electricity, water treatment, or special industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, shipbuilding, and marine engineering, choosing ASME B16.9 SS316 butt weld elbow can provide reliable protection for your pipeline system and help your industrial production operate safely and efficiently.
If you want to know detailed prices and customized solutions for stainless steel butt weld pipe fittings, please feel free to contact us at any time. Our professional sales team will quickly respond to your needs and provide you with convenient inquiry services. We look forward to working together with you to build high-quality pipeline projects!