

Views: 2 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-11 Origin: Site











There are many standards related to forged steel flanges worldwide, among which ASME B16.5 and EN1092-1 are the two most widely used standards worldwide. These standards provide authoritative data parameters for flange production, selection, and application, and provide standard basis for forging flanges to adapt to various types of industrial pipeline systems.
ASME B16.5, developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, is an internationally recognized standard for pipeline flanges and flange fittings, applicable to carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy flanges with nominal pressures ranging from Class 150 to Class 2500 and nominal diameters ranging from 1/2 to 24 inches (corresponding to DN15-DN600).
This standard has strict regulations on the dimensional accuracy, material selection, and pressure and temperature ratings of flanges, ensuring stable operation of flanges in harsh working environments such as high pressure and high temperature.
ASME B16.5 covers various types of flanges, including SW Flange, TH Flange, WN Flange, SO Flange, BL Flange, LAPJ Flange. Among them, socket flanges and threaded flanges are widely used in medium and low pressure pipeline systems as types that do not require full penetration welding. The standards clearly specify the socket size, thread specifications (such as NPT thread, BSPT thread), and sealing surface types (such as RF protruding surface, FF full plane) of both.
EN1092-1 is a pipeline flange standard developed by the European Committee for Standardization, applicable to flanges with nominal pressures ranging from PN 2.5 to PN 400 and nominal diameters ranging from DN 10 to DN 4000. The covering materials include carbon steel (such as P250GH, P280GH), stainless steel (such as 1.4301, 1.4401), and nickel alloy materials. Compared with ASME B16.5, EN1092-1 has differences in pressure rating labeling (using PN series), flange dimension labeling (with DN as the core), and some technical requirements, but its core goal is also to ensure the structural strength and sealing performance of the flange.
EN1092-1 includes product types similar to ASME B16.5, mainly including plate flanges (Type 01), threaded flanges (Type 02), loose fitting flanges, butt welding flanges (Type 11), flat flanges (Type 12), blind flanges (Type 05), etc. At present, EN1092-1 is not only widely used in various European countries, but also widely adopted in Southeast Asia, the Middle East and other regions that have trade relations with Europe.
Socket weld flange is a type of flange that is inserted into a flange socket through a pipeline and fixed by welding. The core structure consists of a flange with a socket, a sealing surface, and bolt holes.
There are various types of sealing surfaces for socket flanges, including raised face (RF), full face (FF), raised face (MFM), etc. Among them, raised face sealing surfaces are widely used in industrial pipelines due to their easy processing and strong adaptability. From a material perspective, socket flanges can be made of carbon steel (such as ASTM A105), stainless steel (such as ASTM A182 F304, F316), or alloy materials according to the characteristics of the medium, to meet different corrosion and temperature environment requirements.
Size | 1/2"- 3" / DN15 - DN80 |
Pressure | Class 150, 300, 600,1500 |
Standard | ASME B16.5/EN1092-1 |
Carbon Steel | ASTM A105, 20#,ASTM A350 LF2, 16Mn,ASTM A694 F42 / 46 / 56 / 60 / 65 |
Alloy Steel | ASTM A182 F11 / 12 / 5 / 9 / 91 / 92 |
Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F304/304L/304H, 316/316L, 310S, 317,347,904L |
Duplex Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F51, F53, F44 |
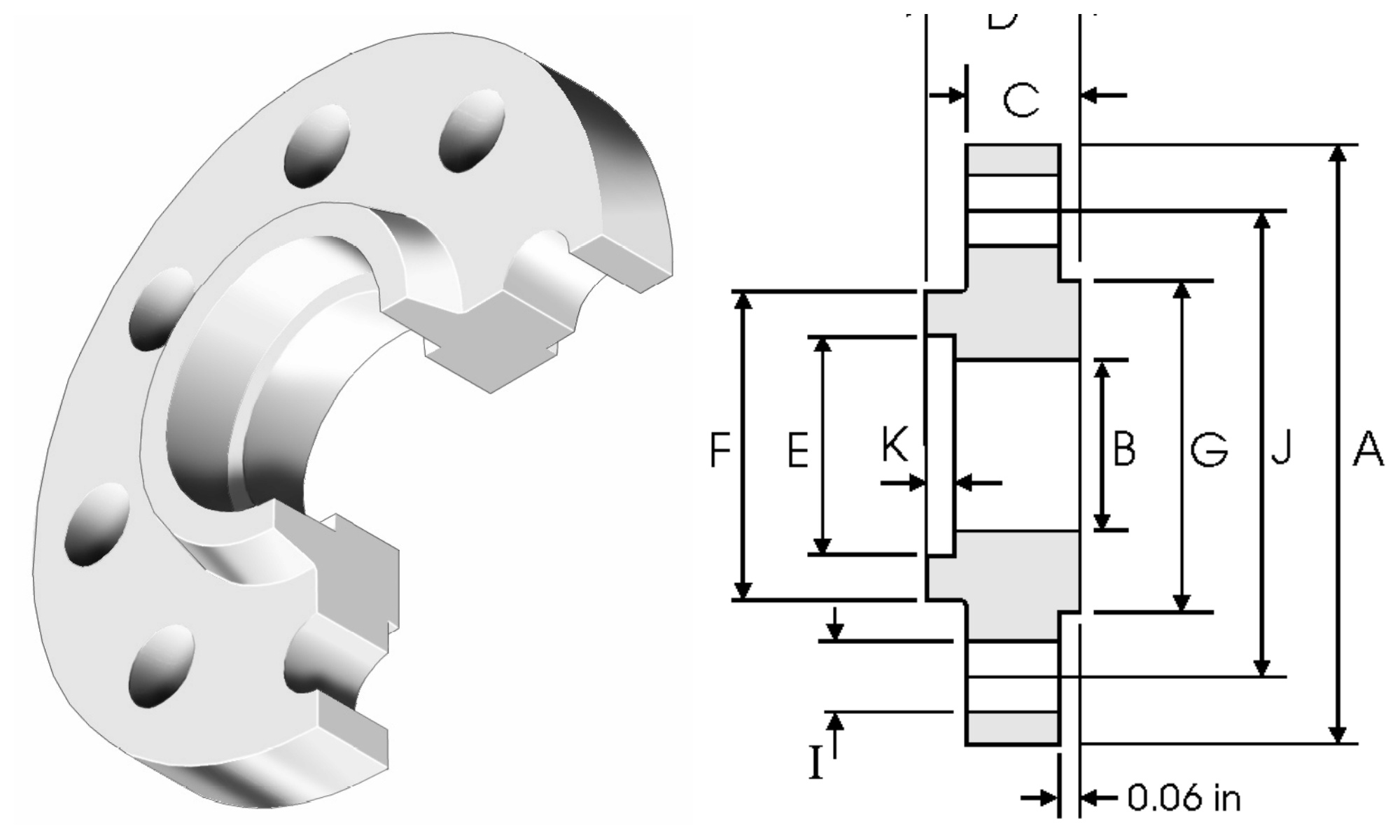
NPS | A | B | C | D | E | K | F | G | H | I | J | W |
inch | inch | inch | inch | inch | inch | inch | inch | No. of Holes | inch | inch | kg/pc | |
mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | |||
1/2 | 3.5 | 0.62 | 0.44 | 0.62 | 0.88 | 0.38 | 1.19 | 1.38 | 4 | 0.62 | 2.38 | 0.42 |
88.9 | 15.7 | 11.2 | 15.7 | 22.4 | 9.6 | 30.2 | 35.1 | 15.7 | 60.45 | |||
3/4 | 3.88 | 0.82 | 0.5 | 0.62 | 1.09 | 0.44 | 1.5 | 1.69 | 4 | 0.62 | 2.75 | 0.59 |
98.6 | 20.8 | 12.7 | 15.7 | 27.7 | 11.1 | 38.1 | 42.9 | 15.7 | 69.85 | |||
1 | 4.25 | 1.05 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 1.36 | 0.50 | 1.94 | 2.0 | 4 | 0.62 | 3.120 | 0.81 |
108 | 26.7 | 14.2 | 17.5 | 34.5 | 12.70 | 49.3 | 50.8 | 15.7 | 79.25 | |||
1¼ | 4.62 | 1.38 | 0.62 | 0.81 | 1.7 | 0.56 | 2.31 | 2.5 | 4 | 0.62 | 3.5 | 1.07 |
117.3 | 35.1 | 15.7 | 20.6 | 43.2 | 14.2 | 58.7 | 63.5 | 15.7 | 88.9 | |||
1½ | 5.0 | 1.61 | 0.69 | 0.88 | 1.95 | 0.62 | 2.56 | 2.88 | 4 | 0.62 | 3.88 | 1.36 |
127 | 40.9 | 17.5 | 22.3 | 49.5 | 15.7 | 65.0 | 73.15 | 15.7 | 98.6 | |||
2 | 6.0 | 2.07 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 2.44 | 0.69 | 3.06 | 3.62 | 4 | 0.75 | 4.75 | 2.10 |
152.4 | 52.6 | 19.1 | 25.4 | 62.0 | 17.5 | 77.7 | 91.9 | 19.1 | 120.7 | |||
2½ | 7.0 | 2.47 | 0.88 | 1.12 | 2.94 | 0.75 | 3.56 | 4.12 | 4 | 0.75 | 5.5 | 3.33 |
177.8 | 62.7 | 22.4 | 28.4 | 74.7 | 19.0 | 90.4 | 104.6 | 19.1 | 139.7 | |||
3 | 7.5 | 3.07 | 0.94 | 1.19 | 3.57 | 0.81 | 4.25 | 5.0 | 4 | 0.75 | 6.0 | 3.90 |
190.5 | 78.0 | 23.9 | 30.2 | 90.7 | 20.6 | 108. | 127 | 19.1 | 152.4 |
The above are the detailed parameters of Class 150 socket weld flanges. Socket weld flanges can be divided into Class 150, Class 300, Class 600, and Class 1500 according to pressure levels. If you need to view other product parameters, please click on the following link:
ASME/ANSI B16.5 150&300lbs Socket Weld Flange
ASME/ANSI B16.5 600&1500lbs Socket Weld Flange
Threaded flange is a type of flange that is connected by screwing the external threads of the pipeline with the internal threads of the flange. Its main structure includes a flange with internal threads, a sealing surface, and bolt holes.
Size | 1/2"- 24"/ DN15 - DN600 |
Pressure | Class 150,300,600,900,1500,2500 |
Standard | ASME B16.5 |
Carbon Steel | ASTM A105, 20#,ASTM A350 LF2, 16Mn,ASTM A694 F42 / 46 / 56 / 60 / 65 |
Alloy Steel | ASTM A182 F11 / 12 / 5 / 9 / 91 / 92 |
Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F304/304L/304H, 316/316L, 310S, 317,347,904L |
Duplex Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F51, F53, F44 |
The thread specifications of the threaded flange need to be strictly matched with the pipeline thread. Common ones include American taper pipe thread (NPT), British pipe thread (BSPT), metric thread (M), etc. Different thread types have different tooth angles and pitches, and cannot be mixed.
In terms of sealing surface design, threaded flanges and socket flanges are basically the same, mainly using raised surfaces (RF), and some high-pressure scenarios may use raised surfaces (MFM).
In terms of material selection, threaded flanges also include carbon steel, stainless steel, alloys, etc., and do not require welding.
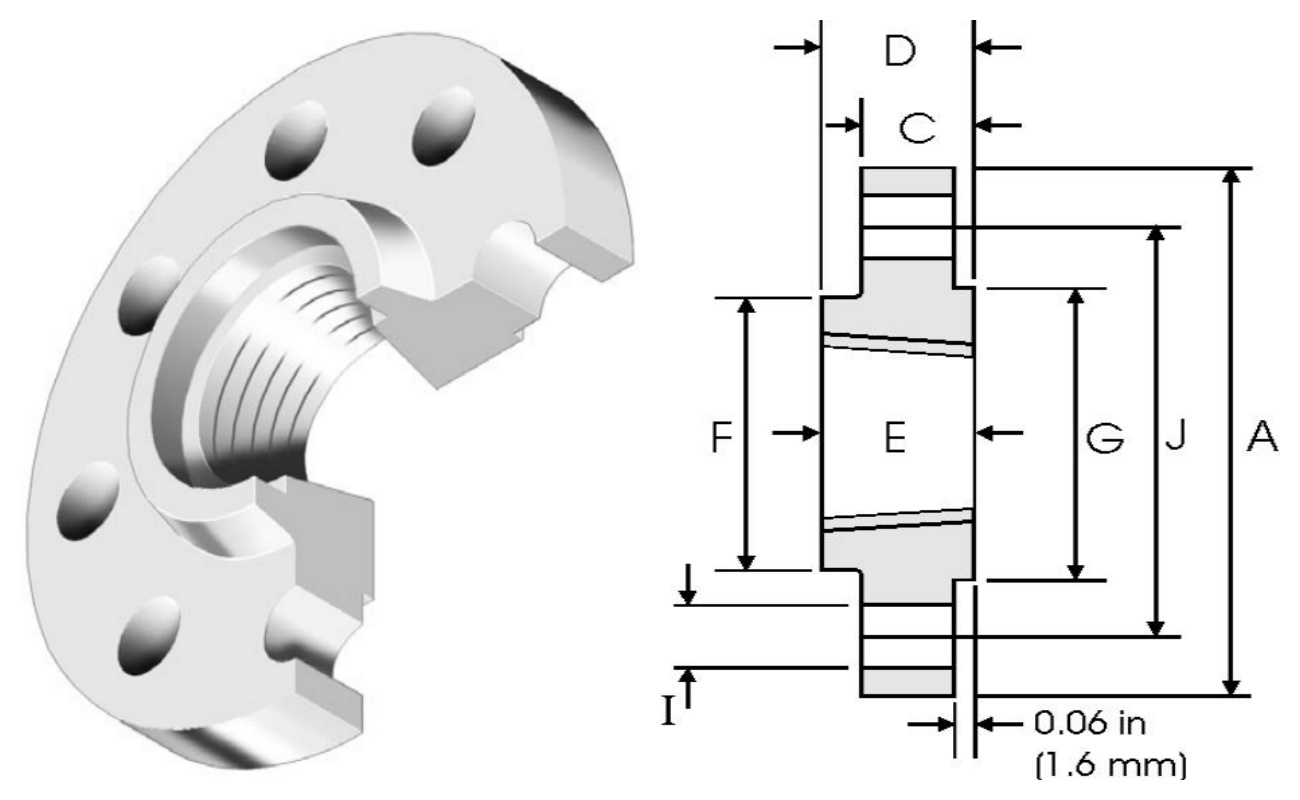
NPS | A | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | W |
inch | inch | inch | inch | inch | inch | No. of Holes | inch | inch | kg/pc | |
mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | |||
1/2 | 3.500 | 0.440 | 0.620 | 0.620 | 1.190 | 1.380 | 4 | 0.620 | 2.380 | 0.39 |
88.9 | 11.20 | 15.70 | 15.70 | 30.20 | 35.10 | 15.70 | 60.45 | |||
3/4 | 3.880 | 0.500 | 0.620 | 0.620 | 1.500 | 1.690 | 4 | 0.620 | 2.750 | 0.56 |
98.60 | 12.70 | 15.70 | 15.70 | 38.10 | 42.90 | 15.70 | 69.85 | |||
1 | 4.250 | 0.560 | 0.690 | 0.690 | 1.940 | 2.000 | 4 | 0.620 | 3.120 | 0.78 |
108.0 | 14.20 | 17.50 | 17.50 | 49.30 | 50.80 | 15.70 | 79.25 | |||
1¼ | 4.620 | 0.620 | 0.810 | 0.810 | 2.310 | 2.500 | 4 | 0.620 | 3.500 | 1.03 |
117.3 | 15.70 | 20.60 | 20.60 | 58.70 | 63.50 | 15.70 | 88.90 | |||
1½ | 5.000 | 0.690 | 0.880 | 0.880 | 2.560 | 2.880 | 4 | 0.620 | 3.880 | 1.32 |
127.0 | 17.50 | 22.40 | 22.30 | 65.00 | 73.15 | 15.70 | 98.60 | |||
2 | 6.000 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 3.060 | 3.620 | 4 | 0.750 | 4.750 | 2.06 |
152.4 | 19.10 | 25.40 | 25.40 | 77.70 | 91.90 | 0.750 | 4.750 | |||
2½ | 7.000 | 0.880 | 1.120 | 1.120 | 3.560 | 4.120 | 4 | 0.750 | 5.500 | 3.28 |
177.8 | 22.40 | 28.40 | 28.40 | 90.40 | 104.6 | 19.10 | 139.7 | |||
3 | 7.500 | 0.940 | 1.190 | 1.190 | 4.250 | 5.000 | 4 | 0.750 | 6.000 | 3.85 |
190.5 | 23.90 | 30.20 | 30.20 | 108.0 | 127.0 | 19.10 | 152.4 | |||
3½ | 8.500 | 0.940 | 1.250 | 1.250 | 4.810 | 5.500 | 8 | 0.750 | 7.000 | 4.81 |
215.9 | 23.90 | 31.75 | 31.75 | 122.2 | 139.7 | 19.10 | 177.8 | |||
4 | 9.000 | 0.940 | 1.310 | 1.310 | 5.310 | 6.190 | 8 | 0.750 | 7.500 | 5.30 |
228.6 | 23.90 | 33.30 | 33.30 | 134.9 | 157.2 | 19.10 | 190.5 | |||
5 | 10.00 | 0.940 | 1.440 | 1.440 | 6.440 | 7.310 | 8 | 0.880 | 8.500 | 6.07 |
254.0 | 23.90 | 36.60 | 36.60 | 163.6 | 185.7 | 22.4 | 215.9 | |||
6 | 11.00 | 1.000 | 1.560 | 1.560 | 7.560 | 8.500 | 8 | 0.880 | 9.5 | 7.45 |
279.4 | 25.40 | 39.60 | 39.60 | 192.0 | 215.9 | 22.40 | 241.3 | |||
8 | 13.50 | 1.120 | 1.750 | 1.750 | 9.690 | 10.62 | 8 | 0.880 | 11.75 | 12.1 |
342.9 | 28.40 | 44.50 | 44.50 | 246.1 | 269.7 | 22.40 | 298.5 | |||
10 | 16.00 | 1.190 | 1.940 | 1.940 | 12.00 | 12.75 | 12 | 1.000 | 14.25 | 16.5 |
406.4 | 30.20 | 49.30 | 49.30 | 304.8 | 323.9 | 25.40 | 362.0 | |||
12 | 19.00 | 1.250 | 2.190 | 2.190 | 14.38 | 15.00 | 12 | 1.000 | 17.00 | 26.2 |
482.6 | 31.75 | 55.60 | 55.60 | 365.3 | 381.0 | 25.40 | 431.8 | |||
14 | 21.00 | 1.380 | 2.250 | 2.250 | 15.75 | 16.25 | 12 | 1.120 | 18.75 | 34.6 |
533.4 | 35.10 | 57.15 | 57.15 | 400.1 | 412.7 | 28.40 | 476.3 | |||
16 | 23.50 | 1.440 | 2.500 | 2.500 | 18.00 | 18.50 | 16 | 1.120 | 21.25 | 44.8 |
596.9 | 36.60 | 63.50 | 63.50 | 457.2 | 469.9 | 28.40 | 539.8 | |||
18 | 25.00 | 1.560 | 2.690 | 2.690 | 19.88 | 21.00 | 16 | 1.250 | 22.75 | 48.9 |
635.0 | 39.60 | 68.30 | 68.30 | 505.0 | 533.4 | 31.75 | 577.9 | |||
20 | 27.50 | 1.690 | 2.880 | 2.880 | 22.00 | 23.00 | 20 | 1.250 | 25.00 | 61.9 |
698.5 | 42.90 | 73.15 | 73.15 | 558.8 | 584.2 | 31.75 | 635.0 | |||
24 | 32.00 | 1.880 | 3.250 | 3.250 | 26.12 | 27.25 | 20 | 1.380 | 29.50 | 86.9 |
812.8 | 47.80 | 82.60 | 82.60 | 663.4 | 692.2 | 35.10 | 749.3 |
The above are the detailed parameters of Class 150 threaded flanges, which can be classified according to pressure levels Class 150,Class 300,Class 400,Class 600,Class 900,Class 1500,Class2500, To view other product parameters, please click on the following link:
ASME/ANSI B16.5 300lbs threaded flange
ASME/ANSI B16.5 400lbs threaded flange
ASME/ANSI B16.5 600lbs threaded flange
ASME/ANSI B16.5 900lbs threaded flange
ASME/ANSI B16.5 1500lbs threaded flange
ASME/ANSI B16.5 2500lbs threaded flange
In terms of connection strength, the socket flange is fixed through pipe insertion into the socket and corner welding. The welding point can transmit axial and radial forces of the pipeline, and the tensile strength can reach more than 80% of the base material. It can stably withstand pressure impact in medium and high pressure pipelines (such as Class 300-Class 600);
Threaded flanges rely on threaded connections, with a smaller force area on the threaded contact surface. Over long-term use, they are prone to thread loosening due to vibration and temperature changes. The connection strength is only 60% -70% of that of socket flanges, making them more suitable for pipeline systems with lower pressure requirements.
In terms of sealing, the socket flange has a dual sealing guarantee: firstly, the welding seal between the pipeline and the socket can prevent the medium from leaking from the gap between the pipeline and the flange; The second is the sealing between the flange surface and the gasket surface, with a large sealing area. After the bolts are evenly tightened, the sealing reliability is high.
The sealing of threaded flanges relies on both threaded sealing and flange surface sealing, making them more suitable for non-toxic and non hazardous media.
In terms of installation difficulty, socket flanges require welding operations, and construction personnel are required to have welding qualifications; At the same time, socket flanges require high straightness of the pipeline, otherwise it will cause the flange surface to be misaligned and affect the sealing.
Threaded flanges do not require welding, only the pipeline threads need to be screwed into the flange threads, and have low requirements for pipeline straightness. They can be installed in scenarios where the pipeline is slightly bent.
In terms of installation efficiency, socket flanges require multiple processes from preparation to installation, resulting in lower installation efficiency; Threaded flanges only require pipe thread processing, and have an advantage in installation efficiency compared to socket flanges.
Suitable for working environments, socket flanges have high connection strength and good sealing performance, and can adapt to corrosive media environments. They are commonly used in core pipeline systems in industries such as petrochemicals, power, and natural gas;
Threaded flanges are limited by connection strength and sealing, and the medium needs to be non-toxic and non corrosive. They are commonly used in municipal water supply, building HVAC, and ordinary industrial auxiliary pipelines.
If the working pressure of the pipeline is ≤ 1.6MPa (Class 150) and the medium is non-toxic and non corrosive, threaded flanges are preferred;
If the working pressure of the pipeline is greater than 1.6MPa (Class 300 and above), or the medium is high-pressure steam or high-pressure gas, a socket flange must be selected.
When transporting toxic, flammable, explosive, and highly corrosive media (such as methanol, sulfuric acid, natural gas), regardless of pressure, it is recommended to choose socket flanges;
When transporting non-toxic, non corrosive, and low viscosity media, if the pressure is ≤ 1.6MPa, threaded flanges can be selected.
If there are no welding conditions on the installation site or frequent disassembly and maintenance are required, threaded flanges can be selected for quick disassembly without welding;
If there are welding conditions at the installation site and the pipeline does not require frequent disassembly during long-term operation, choose socket flanges for a more secure connection and longer service life.
Select based on Standard Adaptability
If the pipeline system follows ASME standards, it is necessary to select socket flanges or threaded flanges that comply with ASME B16.5 standards to ensure compatibility with other fittings;
If the pipeline system follows EN standards, select products that comply with EN1092-1 standards to avoid size mismatches due to differences in standards.
Precautions for the Socket Weld Flanges
1. Welding quality control: Before welding, it is necessary to clean the oil stains and impurities on the pipes and sockets; After welding, a visual inspection is required, and if necessary, penetration testing (PT) should be performed to prevent leakage caused by welding cracks;
2. Pipeline insertion depth: The depth of pipeline insertion into the socket should meet the standard requirements. Insertion too shallow will result in insufficient welding strength, while insertion too deep will affect the flow of the medium and even cause deformation of the flange surface;
3. Bolt tightening requirements: When tightening bolts, a diagonal uniform tightening method should be used to control the tightening torque and avoid uneven torque that may cause deformation of the flange surface and affect the sealing performance;
4. Gasket selection: Select suitable gaskets based on the temperature and pressure of the medium. For example, choose nitrile rubber gaskets for low pressure and room temperature scenarios, graphite composite gaskets, or metal wrapped gaskets for medium high pressure and high temperature scenarios to avoid sealing failure caused by improper gasket materials.
Precautions for Threaded Flanges
1. Thread accuracy and matching: The pipeline thread and flange thread must be strictly matched (such as both NPT threads or BSPT threads), and the thread accuracy must comply with the standard (such as ASME B1.20.1 2A level). After thread processing, the tooth profile must be checked for completeness to avoid thread slippage;
2. Selection of sealing material: Special thread sealant (such as polytetrafluoroethylene sealant) or winding tape should be applied to the threads. When winding tape, it should be clockwise and the winding thickness should be moderate (2-3 turns). Excessive thickness will cause the threads to fail to fit, while insufficient thickness will result in poor sealing;
3. Avoid excessive screwing: When screwing the pipeline into the flange, the screwing depth should be controlled, usually until the flange sealing surface is in contact with the pipeline end face. Excessive screwing can cause damage to the internal threads of the flange, affecting the sealing performance;
4. Vibration protection: If applied to vibration environments (such as pump outlet pipelines), pipe supports should be installed near the threaded flange to reduce the impact of vibration on the threaded connection. At the same time, the thread fastening status should be checked regularly to prevent loosening.
Although socket flanges and threaded flanges belong to the core components of pipeline connections, there are significant differences in structure, performance, and applicable scenarios. By clarifying the requirements of two major standards (ASME B16.5, EN1092-1), scientifically selecting pressure, medium, and installation environment, and strictly following application precautions, we can fully leverage the advantages of both and provide safe and efficient connection solutions for industrial pipeline systems. As a high-end category, forged flanges are indispensable in harsh working conditions and critical scenarios, becoming an important support for ensuring the stable operation of industrial production.