

Views: 15 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-26 Origin: Site












The MSS SP-83 socket weld union, with its unique structural design and easy installation, achieves flexible and reliable connections between pipelines.
The complete union shall consist of three parts: male end, female end, and nut. Equivalent terms are tabulated in Table 3.
Table 3 Terminology of Parts | |
Preferred Term | Equivalent Terms |
Male | Male seat-end Tail Piece-Nut Piece-Coupling-Ball End |
Female | Female seat-end Thread Piece-Body-Head-Cone End |
Nut | Union Coupling Nut-Swivel-Ring |
This design eliminates the need to rotate the entire pipe section like welding or threaded connections to complete connection and disassembly, greatly improving the flexibility and efficiency of pipeline installation and maintenance.
The MSS SP-83 socket joint has a compact structure and regular shape, and the central hex nut provides convenient conditions for installation and disassembly.
MSS SP-83 is an authoritative standard developed by the Standardization Association of Valve and Accessory Manufacturers in the United States. Its full name is "Class 3000 and 6000 Pipe Unions,Socket Welding and Threaded (Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Stainless Steel, and Nickel Alloy)". This standard practice includes the outline and other key dimensions, surface finish, tolerances, testing, marking, material, and performance requirements for pipe joints made of forged carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and nickel alloy, with socket welded or threaded ends.
MSS SP-83 standard practice contains envelope and other essential dimensions, finish, tolerances, testing, marking, material, and minimum performance requirements for forged carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and nickel alloy pipe unions, socket welding and threaded ends.
According to the different end connection methods, the MSS SP-83 standard mainly covers two types:

Socket welding union: Both ends are socket welding interfaces, with high strength and good fatigue resistance.

Threaded union: Both ends or one end are threaded interfaces.
In addition, the material of the joint body and locking nut can be various materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc., to meet the needs of different media and working conditions.
This standard imposes strict requirements on products:
Standard | MSS SP-83 |
Size | 1/8″ TO 3″ |
Pressure | 3000 LBS |
Carbon Steel | ASTM A105 / A105N |
Alloy Steel | ASTM A182 F11 / F12 / F5 / F9 / F91 / F92 / F22 |
Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F304/304L/304H, F316/316L, F310S, F317, F347, F904, F321 |
Duplex Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F51, F53, F44, F55 |
Pressure rating: MSS SP-83 standard specifies that the pressure rating of the flexible joint is divided into two levels, Class 3000 and Class 6000, to meet application requirements.
Material specifications: All component materials must comply with international material standards such as ASTM, such as A105 (carbon steel forgings), A182 F304/F316 (stainless steel forgings), etc., to ensure that the performance of the flexible joint meets the requirements of the working conditions.
Dimensions and tolerances: Accurate tolerance ranges have been established for key dimensions such as total length, socket aperture and depth, and lock nut size.
Marking: Each joint must be clearly marked with the manufacturer, material grade, pressure grade, and size specifications to ensure product traceability.
The dimensions of MSS SP-83 socket joints are designed and manufactured strictly in accordance with standard specifications to ensure their compatibility and interchangeability with piping systems. In terms of dimensional parameters, it mainly includes the aperture, outer diameter, and length of the socket end, the size and thread specifications of the union nut, as well as key dimensions such as the length and height of the overall product; The pressure levels are divided into Class 3000 and Class 6000.
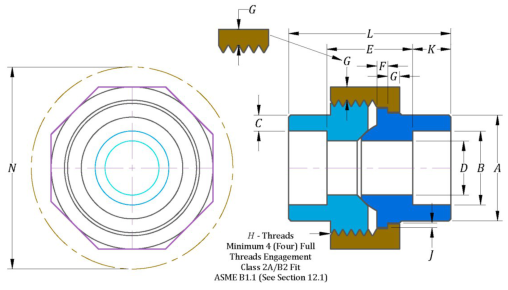
| NPS | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | J | K | L | N |
| Pipe End | Socket Bore Dia. | Socket Wall | Water Way Bore | Laying Length | Male Flange | Nut | Threads per Inch | Bearing | Depth of Socket | Length of Assy. | Clear Assy. Nut | |
| (min) | (min) | (a) | (mm) | (min) | (min) | (min) | (min) | |||||
| 1/8 | 21.8 | 11.18 | 3.18 | 7.59 | 22.4 | 3.18 | 3.18 | 16 | 1.24 | 9.7 | 41.4 | 51 |
| 10.67 | 6.07 | 19.1 | ||||||||||
| 1/4 | 21.8 | 14.61 | 3.3 | 10.01 | 22.4 | 3.18 | 3.18 | 16 | 1.24 | 9.7 | 41.4 | 51 |
| 14.1 | 8.48 | 19.1 | ||||||||||
| 3/8 | 25.9 | 18.03 | 3.51 | 13.28 | 26.9 | 3.43 | 3.43 | 14 | 1.37 | 9.7 | 46 | 56 |
| 17.53 | 11.76 | 20.6 | ||||||||||
| 1/2 | 31.2 | 22.23 | 4.09 | 16.56 | 26.9 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 14 | 1.5 | 9.7 | 49 | 58 |
| 21.72 | 15.04 | 20.6 | ||||||||||
| 3/4 | 37.1 | 27.56 | 4.27 | 21.69 | 31.8 | 4.06 | 4.06 | 11 | 1.68 | 12.7 | 56.9 | 66 |
| 27.05 | 20.17 | 25.4 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 45.5 | 34.29 | 4.98 | 27.41 | 34.3 | 4.57 | 4.45 | 11 | 1.85 | 12.7 | 62 | 79 |
| 33.78 | 25.88 | 26.2 | ||||||||||
| 1-1/4 | 54.9 | 43.05 | 5.28 | 35.81 | 40.6 | 5.33 | 5.21 | 10 | 2.13 | 12.7 | 71.1 | 94 |
| 42.55 | 34.29 | 32.5 | ||||||||||
| 1-1/2 | 61.5 | 49.15 | 5.54 | 41.66 | 42.2 | 5.84 | 5.59 | 10 | 2.31 | 12.7 | 76.5 | 112 |
| 48.64 | 40.13 | 34 | ||||||||||
| 2 | 75.2 | 61.62 | 6.05 | 53.26 | 45.5 | 6.6 | 6.35 | 10 | 2.69 | 15.7 | 86.1 | 132 |
| 61.11 | 51.74 | 37.3 | ||||||||||
| 2-1/2 | 91.7 | 74.45 | 7.67 | 64.24 | 61.7 | 7.49 | 7.11 | 8 | 3.07 | 15.7 | 102.4 | 150 |
| 73.81 | 61.19 | 52.1 | ||||||||||
| 3 | 109.2 | 90.42 | 8.31 | 79.45 | 63.8 | 8.26 | 8 | 8 | 3.53 | 15.7 | 109 | 175 |
| 89.79 | 76.4 | 53.6 |
| NPS | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | J | K | L | N |
| Pipe End | Socket Bore Dia. | Socket Wall | Water Way Bore | Laying Length | Male Flange | Nut | Threads per Inch | Bearing | Depth of Socket | Length of Assy. | Clear Assy. Nut | |
| (min) | (min) | (a) | (mm) | (min) | (min) | (min) | (min) | |||||
| 1/8 | 21.8 | 11.18 10.67 | 3.43 | 4.80 3.20 | 22.4 19.1 | 3.18 | 3.18 | 16 | 1.24 | 9.7 | 41.4 | 51 |
| 1/4 | 25.9 | 14.61 14.10 | 4.01 | 7.11 5.59 | 26.9 20.6 | 3.43 | 3.43 | 14 | 1.37 | 9.7 | 46.0 | 56 |
| 3/8 | 31.2 | 18.03 17.53 | 4.37 | 9.88 8.36 | 26.9 20.6 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 14 | 1.50 | 9.7 | 49.0 | 58 |
| 1/2 | 37.1 | 22.23 21.72 | 5.18 | 12.55 11.02 | 31.8 25.4 | 4.06 | 4.06 | 11 | 1.68 | 9.7 | 56.9 | 66 |
| 3/4 | 45.5 | 27.56 27.05 | 6.05 | 16.31 14.78 | 34.3 26.2 | 4.57 | 4.45 | 11 | 1.85 | 12.7 | 62.0 | 79 |
| 1 | 54.9 | 34.29 33.78 | 6.93 | 21.46 19.94 | 40.6 32.5 | 5.33 | 5.21 | 10 | 2.13 | 12.7 | 71.1 | 94 |
| 11/4 | 61.5 | 43.05 42.55 | 6.93 | 30.23 28.70 | 42.2 34.0 | 5.84 | 5.59 | 10 | 2.31 | 12.7 | 76.5 | 112 |
| 11/2 | 75.2 | 49.15 48.64 | 7.80 | 34.75 33.22 | 45.5 37.3 | 6.60 | 6.35 | 10 | 2.69 | 12.7 | 86.1 | 132 |
| 2 | 91.7 | 61.62 61.11 | 9.50 | 43.61 42.09 | 61.7 52.1 | 7.49 | 7.11 | 8 | 3.07 | 15.7 | 102.4 | 150 |
| 21/2 | 109.2 | 74.45 73.81 | 10.39 | 54.74 53.21 | 63.8 53.6 | 8.26 | 8.00 | 8 | 3.53 | 15.7 | 109.0 | 175 |
The material selection of MSS SP-83 socket weld union directly affects its performance, applicable scenarios, and service life. It needs to be determined comprehensively based on factors such as medium characteristics, operating temperature, pressure level, etc. Common materials mainly include the following categories:
Carbon steel is a widely used basic material in socket joints, with common grades such as A105, Q235, etc. It has the advantages of low cost, stable mechanical properties, good strength and toughness.
Stainless steel material, with its excellent corrosion resistance, has become the core choice for MSS SP-83 socket joints in complex working conditions. Common grades include 304, 316, 316L, etc.
Alloy steel socket joints are mainly designed for high temperature, high pressure, and high-strength working conditions. Common grades such as F11, F22, F91, etc. By adding alloy elements such as chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium to the steel, the high-temperature strength, toughness, and heat fatigue resistance of the material are significantly improved.
Correct installation is the key to ensuring the performance and safety of socket joints. The installation process is simple and efficient:
1. Preparation work: Ensure that the pipeline ports are flat and vertical, and remove impurities such as burrs, oil stains, and oxides on the inside and outside of the ports. Check the inside of the flexible joint to ensure that the sealing surface is clean and undamaged.
2. Pipe insertion and positioning: Insert the two pipes that need to be connected into the socket and plug ends of the joint, and gently push them to the bottom.
3. Spot welding fixation: In order to maintain the relative position between the pipeline and the joint and prevent displacement during final welding, symmetrical spot welding (usually two or four points) should be carried out at the connection between the socket end and the pipeline first.
4. Final welding and fastening: After completing spot welding, use two wrenches, one to fix the joint body and the other to tighten the central locking nut to the specified torque value (if recommended by the manufacturer). Then complete a 360 degree sealing fillet weld around the socket end. After welding is completed, there is no need to tighten the nut again.
Caution: Avoid over tightening the locking nut, as it may cause damage to the sealing surface or thread slippage. Appropriate welding techniques should be used during welding to avoid damage to the material properties of the joint body caused by welding heat.
Among various pipeline connection methods, MSS SP-83 socket joint exhibits unparalleled advantages with its unique design:
1. Installation and maintenance convenience: It is convenient to complete installation or disassembly, saving labor and time costs.
2. Adjustable and Neutral: The pipeline can be fine tuned within a certain range to reduce installation stress.
3. Compact structural design: The structure of the flexible joint is very compact, occupying little space and being lightweight, making the pipeline layout more flexible.
4. Reliable sealing performance: The independent mechanical sealing mechanism does not rely on welding sealing, providing dual sealing guarantee.
5. Standardization and Interchangeability: Following MSS SP-83 standard ensures the availability of spare parts and system compatibility, reducing lifecycle costs.
6. Reduce potential leakage points
MSS SP-83 socket weld union is not only a simple pipeline component, but also a perfect embodiment of the flexibility, reliability, and efficient maintenance concepts in modern industrial pipeline design. Choosing products that comply with MSS SP-83 standards is choosing a time tested guarantee for your pipeline system, ensuring long-term, stable, and safe operation of the system.