

Views: 23 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-17 Origin: Site











SS304 threaded coupling is an important component of pipeline connection fittings, which plays a key role in the reliability, safety, and durability of industrial pipeline connections due to its excellent performance and wide applicability.
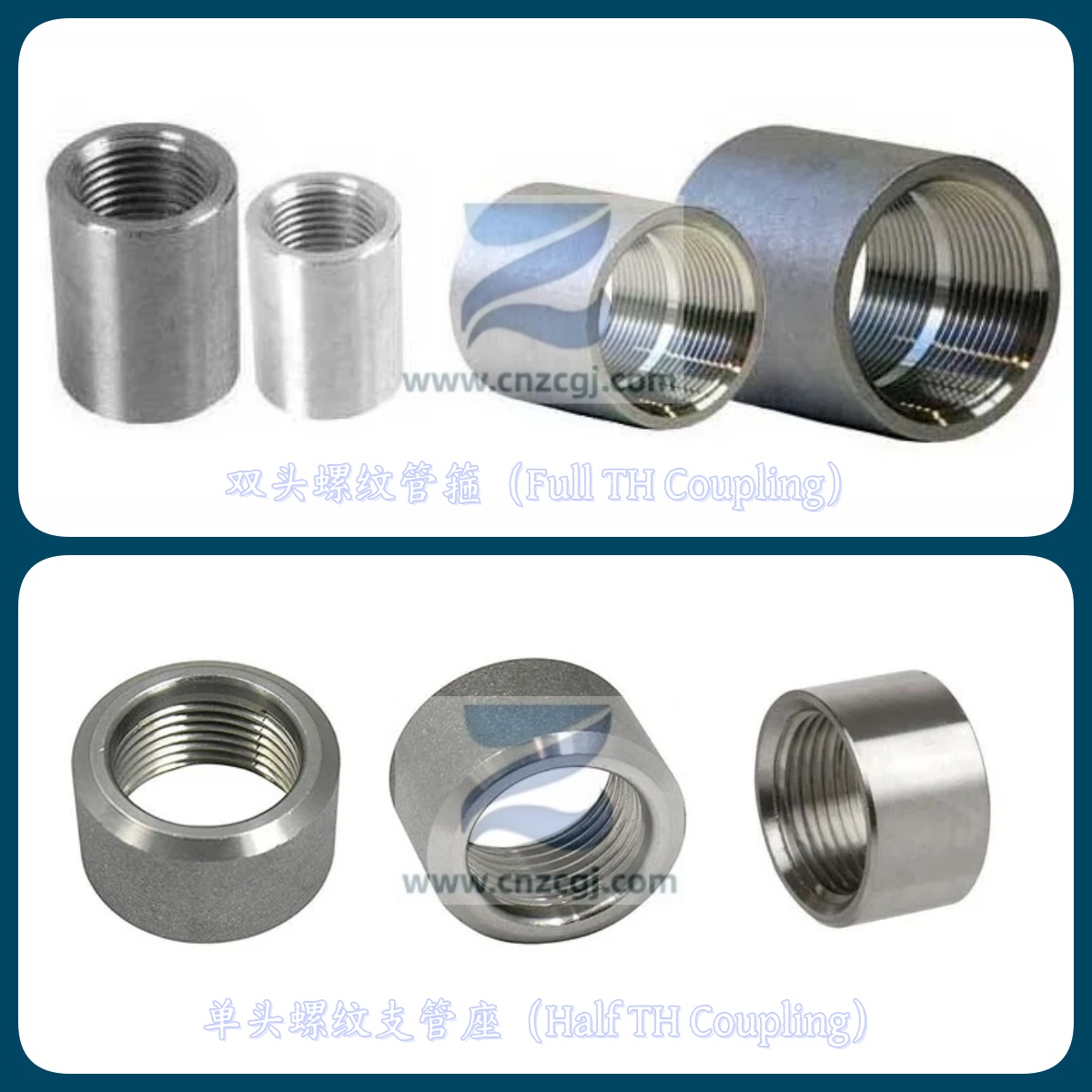
SS304 threaded coupling is a pipe accessory forged from SS304 stainless steel material and connected to pipelines in a threaded form. It is mainly used for fast and stable connection of two sets of pipelines, playing a key role in connecting the upper and lower parts of the pipeline system.
From the appearance, SS304 threaded couplings usually present a silver white metallic luster, with a smooth and flat surface, and no obvious scratches, dents, or impurities. Its overall shape is generally cylindrical or approximately cylindrical, with precision internal threads machined on the ports. Some couplings have hexagonal or other shaped edges, making it easy to install and disassemble with tools and improving the convenience of operation.
Half Threaded Coupling

Half threaded coupling has threads, and the other end is for other connection forms or used for sealing under specific working conditions.
Full Treaded Coupling

Full threaded coupling has threads on both ends and can be used to connect two pipes of the same specification, enabling quick docking of the pipes.Its symmetrical structural design also ensures the stability and uniformity of the connection.
| Joint Type | Class | Grade of Connecting Pipes | |||||||
| THRD | 2000 |  Sch80 XS Sch80 XS | |||||||
| 3000 | Sch160 | ||||||||
| 6000 | XXS | ||||||||
ASTM A182 is developed by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) specifically for forged alloy and stainless steel fittings, covering various types such as socket fittings and threaded fittings. Simply put, it specifies the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and heat treatment requirements for steel used in the manufacture of flanges, fittings, valves, and other high-pressure and high-temperature pipeline system components.
ASTM A182 forging materials are mainly divided into three categories: alloy, austenitic stainless steel, and duplex stainless steel. Suitable materials can be selected for use according to the specific industrial pipeline working environment. The commonly used materials for stainless steel threaded couplings include not only SS304 stainless steel, but also ASTM A182 F316/F44; Stainless steel grades such as duplex stainless steel F51/F53 have excellent corrosion resistance and high temperature performance, which can meet the needs of different working conditions.
As the core material of SS304 threaded couplings, the performance of SS304 stainless steel directly determines the quality and applicable scenarios of the couplings, which is the key difference from ordinary carbon steel and other grades of stainless steel pipe fittings.
Chemical Composition
| CHEMICAL | LIMITS | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Ni | Cr | N |
| ASTM A182 F304 | MIN | 8.00 | 18.00 | ||||||
| MAX | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 11.00 | 20.00 | 0.10 | |
| ASTM A182 F304L | MIN | 8.00 | 18.00 | ||||||
| MAX | 0.03 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 13.00 | 20.00 | 0.10 |
Chromium is the core element that endows it with corrosion resistance - chromium forms a dense chromium oxide (Cr ₂ O3) passivation film on the surface of the material, which can firmly adhere to the metal surface and quickly self repair even if locally damaged, effectively isolating the erosion of air, moisture, and corrosive media; Nickel element can stabilize the austenite structure, improve the toughness, ductility, and low-temperature impact resistance of the material, and further enhance the corrosion resistance, allowing SS304 stainless steel to maintain stable performance in various complex environments.
Mechanical Properties
| MATERIAL | T.S (MPA) | Y.S (MPA) | EL % | R/A % |
| ASTM A182 F304 | 515 min | 205 min | 30 min | 50 min |
| ASTM A182 F304L | 485 min | 170 min | 30 min | 50 min |
In terms of core performance, SS304 stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties, excellent temperature resistance, and hygiene and safety.
The production standards for forged pipe fittings cover multiple aspects such as material selection and inspection, forging process control, surface treatment and testing, and quality management system. The strict implementation of these standards is key to ensuring the quality, safety, and applicability of pipe fittings. ASME B16.11, MSS-SP-79, MSS-SP-83, MSS-SP-95, MSS-SP-97, and BS3799 are all production standards for forged fittings.
Forged pipe fittings are made by using forging technology and forging machinery to apply pressure to metal billets, causing them to undergo plastic deformation, thereby obtaining pipes with certain mechanical properties, shapes, and sizes. According to the different varieties and requirements of pipe fittings, forging of pipe fittings mainly adopts forging, free forging, and cutting forming processes. The common types of forged fittings include forged socket fittings and forged threaded fittings. Common production standards for forged pipe fittings include ASME B16.11; MSS SP-83; MSS SP-97; MSS SP-95, etc.
ASME B16.11 standard, as one of the important standards for the production of threaded pipe fittings, has clear and detailed regulations on the size of threaded couplings, ensuring the universality and interchangeability of products. The following will introduce the size requirements of ASME B16.11 threaded couplings from the aspects of nominal size, thread size, length size, etc.
Nominal Size
ASME B16.11 threaded couplings have a wide range of nominal sizes, typically covering various specifications from 1/8 inch to 4 inches, to meet the connection requirements of different piping systems. The nominal size is the basic dimensional parameter of the threaded coupling, representing the specification size of the coupling. When selecting, users need to match it according to the nominal size of the connected pipeline to ensure compatibility of the connection.
Length of Thread
The thread size is one of the key dimensions of ASME B16.11 threaded couplings, which directly affects the sealing and firmness of the connection. The standard strictly specifies the dimensional parameters of thread profile, pitch, tooth height, major diameter, minor diameter, etc. Common thread types include NPT (American Standard Cone Pipe Thread), NPSM (American Standard Mechanical Straight Pipe Thread), etc. Different thread types are suitable for different pressure and medium conditions. For example, NPT threads have a conical structure that can achieve self sealing during the connection process, making them suitable for medium and high pressure pipeline systems; NPSM thread is a straight pipe thread that usually requires the use of sealing gaskets and is suitable for low-pressure pipeline systems.
End-to-End
ASME B16.11 specifies the length dimensions of threaded couplings, and different nominal sizes of couplings correspond to different length requirements. The length dimensions mainly include the total length of the coupling, the length of the threaded part, etc. A reasonable length design can ensure that the coupling has sufficient strength and stability after installation, while also being easy to operate and maintain. For example, for couplings with smaller nominal sizes, their total length is relatively short, while for couplings with larger nominal sizes, in order to ensure the reliability of the connection, the total length will increase accordingly.
In addition, ASME B16.11 standard also specifies the wall thickness, chamfer size, and other aspects of threaded couplings to ensure the overall performance and quality of the product. In the actual production process, manufacturers must strictly follow the standard requirements for processing and inspection to ensure that each batch of products meets the size standards and provide users with high-quality threaded coupling products.
Dimension Chart
Nominal Size | End-to-End | Outside Diameter | Length of Thread | |||
DN | NPS | W | D | L 5 min | L 2 min | |
3000 & 6000 | 3000 | 6000 | ||||
6 | 1/8 | 32 | 16 | 22 | 6.4 | 6.7 |
8 | 1/4 | 35 | 19 | 25 | 8.1 | 10.2 |
10 | 3/8 | 38 | 22 | 32 | 9.1 | 10.4 |
15 | 1/2 | 48 | 28 | 38 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
20 | 3/4 | 51 | 35 | 44 | 12.7 | 13.9 |
25 | 1 | 60 | 44 | 57 | 14.7 | 17.3 |
32 | 1¼ | 67 | 57 | 64 | 17.0 | 18.0 |
40 | 1½ | 79 | 64 | 76 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
50 | 2 | 86 | 76 | 92 | 19.0 | 19.2 |
65 | 2½ | 92 | 92 | 108 | 23.6 | 28.9 |
80 | 3 | 108 | 108 | 127 | 25.9 | 30.5 |
100 | 4 | 121 | 140 | 159 | 27.7 | 33.0 |
Weight List (KG)
Nominal Size | THRD Coupling | |
D N | NPS | 6000 |
6 | 1/8 | 0.09 |
15 | 1/2 | 0.40 |
32 | 11/4 | 1.32 |
65 | 21/2 | 4.81 |
The thread form is the core part of the threaded coupling to achieve the connection function. Different thread forms have different characteristics and applicable ranges. Understanding the relevant knowledge of thread forms can help users choose the appropriate threaded coupling according to their actual needs.

The thread form is a key factor affecting the connection performance of threaded couplings. The common thread forms of ASME B16.11 threaded couplings mainly include NPT, BSP, and PT.
NPT: This is a commonly used taper pipe thread with a thread profile of 60 ° and self sealing characteristics. Due to the conical shape of the thread, the tooth sides of the internal and external threads are tightly fitted during the connection process, and a certain sealing effect can be achieved without the need for additional sealing components, making it suitable for medium and low pressure pipeline systems. NPT threads are divided into NPT external threads and NPT internal threads. During installation, attention should be paid to the length and torque control of the threads to ensure sealing performance and connection strength.
BSP : BSP is the overall code for British pipe threads, but it is divided into three types: BSPP, BSPT, and BSPF.
BSPP is the code for British cylindrical pipe threads, with only internal threads, equivalent to 55 degree cylindrical (parallel) pipe threads in China;
BSPT: It is a British conical pipe thread standard, which refers to a thread profile angle of 55 degrees and a taper of 1:16,
BSPF: for British fine tooth pipe threads; The first two are used for sealing joints, while the latter one is used for general joints.
Compared with NPT threads, BSPT threads have different pitch and size specifications, and are mainly widely used in Europe and Commonwealth countries. When selecting, it is necessary to determine the appropriate thread form based on the design standards of the pipeline system and the region of use, to ensure compatibility and reliability of the connection.
PT : It is a 55 degree sealed conical pipe thread, belonging to the Wyeth thread family, commonly used in Europe and federal countries, commonly used in the water and gas pipe industry, with a taper of 1:16. The marking of pipe threads consists of thread characteristic code (R) and size code. R1/2 represents an R thread with a thread size of 1/2.
Building materials field
Petrochemical industry
Food and pharmaceutical field
Water treatment field
other fields